Imperfect or past tense? The difference between these two past tenses
Are you learning French and wondering when to use the imperfect tense or the passé composé? These two past tenses often pose problems, even for advanced learners. However, mastering them allows you to accurately describe what you did, saw, experienced, etc. This article clearly explains the difference between the imperfect tense and the passé composé, with simple, concrete examples.
When to use the imperfect tense?
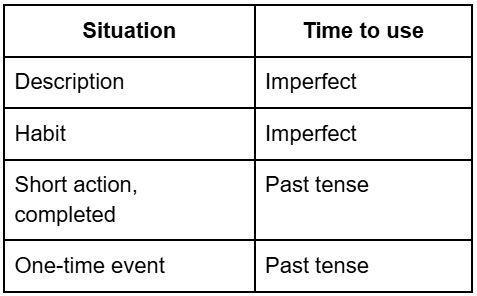
The imperfect tense is used to describe the past: a habit, a long action or a context.
Here are the main cases where you should use the imperfect:
- • A repetitive or habitual action in the past:
→ Quand j’étais enfant, je jouais tous les jours au foot. - • A description or situation:
→ Il faisait beau, les oiseaux chantaient. - • An action in progress in the past, without a specified beginning or end:
→ Je lisais un livre quand le téléphone a sonné.
The imperfect tense often provides an atmosphere, a setting. It tells what was there in the background.
When to use the past tense?
The past tense is used to describe completed actions, often brief and precise.
Here’s when to use it:
- • A one-off action, completed:
→ Hier, j’ai vu un film au cinéma. - • An event or change:
→ Elle est arrivée à 8 heures. - • A series of successive actions:
→ Il s’est levé, il a pris une douche, puis il est parti.
The past tense moves the story forward. It marks important events, what really happened.
Imperfect and past perfect in the same story
Both tenses can be used together, in the same paragraph. And this is often where the confusion begins.
A simple example:
Je marchais dans la rue (imperfect), quand soudain j’ai entendu un bruit (past tense).
Here :
- • Imperfect = action in progress / setting
- • Past tense = sudden action / event
Another example:
Il faisait froid, la neige tombait doucement. Soudain, la porte s’est ouverte.
The imperfect tense sets the scene. The past tense describes what interrupts or changes the situation.
How to avoid making mistakes?
Here are some simple tips to avoid confusing the two tenses:
- • Ask yourself: Is this action finished and punctual? → Past tense
- • Or: Am I describing an atmosphere, a habit, a long action? → Imperfect
➡️ Visual reminder:
And above all: practice regularly, the ear gets used to it over time.
In summary: what is the difference between the imperfect and the past tense?
- • Imperfect: context, description, habit, current action.
- • Past tense: completed action, specific event, change.
They don’t oppose each other; they complement each other. The imperfect tense sets the scene, the past tense moves the action forward.
Conclusion
Choosing between the imperfect and the passé composé is a key step in improving your French speaking and writing skills. It allows you to better share your memories, experiences, and stories.
By understanding the logic of each tense, you’ll gain precision and fluency. And most importantly, don’t worry if you still make mistakes—it’s normal. What matters is practicing again and again!
Guide for beginners
French: where to start?
This guide with the basics of French will allow you to:
✨ Know how to get started learning French
✨ Quickly acquire basic conversational skills
✨ Be able to get by during a first trip to France
Ready to start your apprenticeship? Let’s go !

Information
Legal notice
GTC
Customer reviews
FAQ

